Contacts
Contacts are a system that allows avatars and worlds to detect collisions with other contacts. You can use collisions to drive avatar and world behavior to perform all sorts of custom interactions.
These are separate from standard Unity colliders. Contacts are broken down into senders and receivers. Senders simply exist to be detected. Receivers detect senders and then update parameters or trigger events accordingly.
When using contacts on an avatar, the amount of contacts you use will affect its performance rank.
VRCContactSender
The Contact Sender component defines a volume of space that will send a Contact signal upon contact with a Contact Receiver.
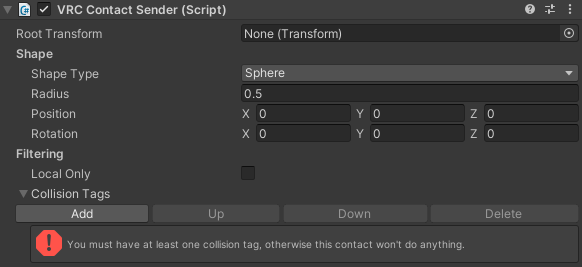
Root Transform- Transform where this contact is placed. If empty, we use this GameObject's transform.
Shape
This section contains settings that define the shape of the ContactSender.
Shape Type- Type of collision shape used by this contact. You can choose between Sphere and Capsule.Radius- Size of the collider extending from its origin.Height- Height of the capsule along the Y axis, including the half-spheres at each end. Only used when Shape Type is set to Capsule.Position- Position offset from the root transform.Rotation- Rotation offset from the root transform.
Contact shapes are limited to a maximum radius of 3 meters and a maximum height of 6 meters. If the contact is attached to a scaled game object, these limits are applied after scaling.
Filtering
This section contains settings allowing you to adjust and define how this ContactSender will interact with ContactReceivers.
Local Only- Available to Contact Senders on avatars only. Limit this contact to only work on the local client. If enabled, the contact doesn't reduce your avatar's performance rank.Content Types- Available to Contact Senders in worlds only. Allows you to set whether this Contact Sender triggers Contact Receivers in worlds, on avatars, and/or items.Collision Tags- List of strings that specify what it can affect/be affected by. For a successful collision to occur, both the sender and receiver need at least one matching pair of strings. Collision tags are case-sensitive. A Contact can have up to 16 tags.
As an example, the tags below will cause the Sender to send a contact signal when they come into contact with the default Head ContactReceiver or any custom ContactReceiver with the tag Face - note the capital F!
You can use whatever text you'd like as a tag, but the SDK also provides a list of suggested tags that you can use to make it easier to make contact systems that work with avatars and worlds you didn't make yourself. See Built-In Contact Tags for more information.
If you decide to use custom collision tags, it's recommended that you write them in PascalCase, to match how the built-in tags are formatted.
Standard Colliders
On avatars, a set of "Standard Colliders" are defined in the Avatar Descriptor, in a section called “Colliders”. This section lets you define a number of standard colliders that exist on every avatar. These will be setup automatically if you don’t touch this, but they may also be tweaked to exactly fit your avatar. These colliders do not affect the performance rating.
- Head
- Torso
- Hands L/R
- Feet L/R
- Fingers L/R
- Index
- Middle
- Ring
- Little
These colliders act primarily as Contact Senders using the built-in body part tags that other people can detect with their avatars. However, the finger and hand colliders are also used to create global PhysBone Colliders that can be used to affect other people’s PhysBones as well as PhysBones in the world.
VRCContactReceiver
The Contact Receiver component defines a volume of space that will receive a Contact signal upon contact with a Contact Sender.
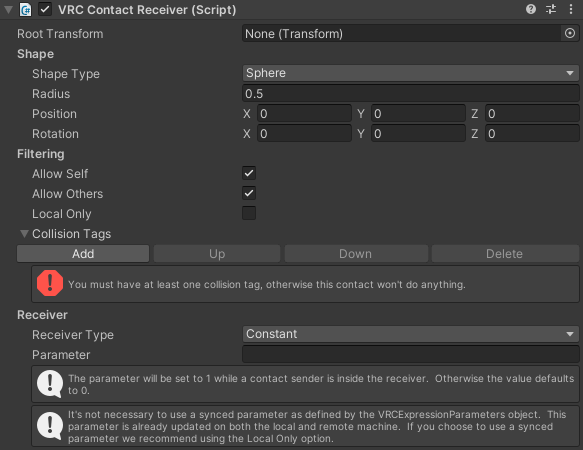
Root Transform- Transform where this contact is placed. If empty, we use this GameObject's transform.
What happens when a Contact Receiver receives a signal from a Contact Sender depends on what the Contact Receiver belongs to:
- If the Contact Receiver is part of an avatar, it sets an Animator Parameter in a certain way, as defined by the avatar author.
- If the Contact Receiver is part of a world, it instead triggers one of the following events on all Udon behaviors that are attached to the same GameObject as the Receiver:
OnContactEnter(ContactEnterInfo contactInfo)- Event raised as the Contact Sender starts contacting the Contact Receiver.OnContactExit(ContactExitInfo info)- Event raised as the Contact Sender stops contacting the Contact Receiver.
Shape
This section contains settings that define the shape of the ContactReceiver.
Shape Type- Type of collision shape used by this contact.Radius- Size of the collider extending from its origin.Height- Height of the capsule along the Y axis, including the half-spheres at each end. Only used when Shape Type is set to Capsule.Position- Position offset from the root transform.Rotation- Rotation offset from the root transform.
Contact shapes are limited to a maximum radius of 3 meters and a maximum height of 6 meters. If the contact is attached to a scaled game object, these limits are applied after scaling.
Filtering
This section contains settings allowing you to adjust and define how this ContactReceiver will interact with ContactSenders.
Allow Self- Available to Contact Receivers on avatars only. Allow this contact to be affected by yourself.Allow Others- Available to Contact Receivers on avatars only. Allow this contact to be affected by other people.Local Only- Available to Contact Receivers on avatars only. Limit this contact to only work on the local client. If enabled, the contact doesn't reduce your avatar's performance rank.- You may use up to 256 contact components on a single avatar by enabling this option. If you exceed this limit, you cannot upload the avatar.
Content Types- Available to Contact Receivers in worlds only. Allows you to set whether this Contact Receiver triggers Contact Receivers in worlds, on avatars, and/or items.Collision Tags- List of strings that specify what it can affect/be affected by. For a successful collision to occur, both the sender and receiver need at least one matching pair of strings. Collision tags are case-sensitive. A Contact can have up to 16 tags.
Receiver
This section contains settings defining what the Receiver does when it gets a signal.
Receivers on Avatars
When used on an avatar, a Contact Receiver will respond to contact signals by setting Animator Parameter in the avatar's animator.
Receiver Type defines the behavior of the parameter setting when a signal is received.
Constant- Informs you when any contacts are present. Resets when no contact is detected. Ideally, use a bool parameter here. Sets1.0for a Float,Truefor a Bool, and1for an Int.OnEnter- Informs you the frame a contact is detected. Resets immediately the next frame. Ideally, use a bool parameter here. Sets1.0for a Float,Truefor a Bool, and1for an Int. Can optionally have aMin Velocitydefined.Proximity- Gives you a Float value of0.0-1.0depending on how close a contact is to the trigger's center. This is calculated as the closest point of the sender onto the receiver. You must use a Float. If multiple contacts are detected, it will give you the closest.Parameter- The parameter updated on the animation controller. This parameter DOES NOT need to be defined on the synced Avatar Parameter list. The parameter can be a Float, Bool, or Int, depending on the Receiver Type used.Value- Value the parameter is updated to when a collision is detected. Parameter will reset to zero when no collisions are present.Min Velocity- Minimum velocity needed from an incoming collider to affect this trigger, only active inOnEntertype.
Receivers in Worlds
Contact Receiver components in worlds offer no configuration options. Instead, Receivers always respond to contact signals by invoking events in any Udon scripts attached to the same GameObject as the Receiver. See the section below for more info about interacting with contacts using Udon.
Udon Access in Worlds
- You can create fields and variables that reference Contact Senders and Contact Receivers in your world using the types
VRCContactSenderandVRCContactReceiverrespectively. Both of these classes are in the namespaceVRC.SDK3.Dynamics.Contact.Components. - To detect when a Contact Sender and Contact Receiver come together, you can attach an UdonGraph or UdonSharp behaviour to the same game object as the Contact Receiver component and use the following events:
OnContactEnter(ContactEnterInfo contactInfo)- Called when a Contact Sender starts contacting the Contact Receiver. The parameter is a data structure containing this information about the contact:ContactSenderProxy contactSender- A reference to the Contact Sender component involved in this collision.ContactReceiverProxy contactReceiver- A reference to the Contact Receiver component involved in this collision.Vector3 enterVelocity- The relative velocity of the Contact Sender against the Contact Receiver at the point of contact.Vector3 contactPoint- The estimated point of contact on the surface of the Contact Receiver, in world space.string[] matchingTags- An array of the tags that the Contact Sender and Contact Receiver have in common.
OnContactExit(ContactExitInfo contactInfo)- Called when a Contact Sender stops contacting the Contact Receiver. Like with the enter event, the parameter is a data structure that has some information about the collision:ContactSenderProxy contactSender- A reference to the Contact Sender component involved in this collision.ContactReceiverProxy contactReceiver- A reference to the Contact Receiver component involved in this collision.string[] matchingTags- An array of the tags that the Contact Sender and Contact Receiver have in common.
- In each of above events,
contactSenderandcontactReceiverare proxy objects referencing the Contact Sender and Contact Receiver involved in the collision. You can check if these match aVRCContactSenderorVRCContactReceiverin your world by comparing the two objects using==or!=. The proxy object itself contains the following properties:bool isValid- True if this proxy object is referring to a valid contact component, false if it isn't. You should check that this is true before accessing any of the other properties.VRCPlayerApi player- A reference to the player that owns the contact component, if applicable. For contact components in the world, this value will be null.DynamicsUsage usage- Describes what kind of content the contact component belongs to. This will beWorldfor any contacts that are part of your world, andAvatarfor any that are part of an avatar.Vector3 position- The world space position of the contact component's root transform.Quaternion rotation- The world space rotation of the contact component's root transform.Vector3 scale- The lossy scale of the contact component's root transform.
- You can read and set the
radius,height,positionandrotationproperties of a Contact Sender or Contact Receiver by getting and setting those fields.- If you ever change these properties, you must also call
ApplyConfigurationChanges()on the Contact after you've finished making all of your changes, otherwise they won't actually be applied back to the Contact. - Configuration changes to Contacts can get expensive! If you overdo it, you might cause performance problems that make your world uncomfortable for players - avoid changing these properties too frequently, and try to batch together as many changes as possible before applying them.
- If you ever change these properties, you must also call
- At any time, you can calculate the proximity between a Receiver and a Sender using the method
CalculateProximity()on the Receiver. This returns a Float value from0.0-1.0representing how close the Sender is to the Receiver's center. - You can change the set of allowed content types and collision tags for a Contact by using the methods
UpdateContentTypes(DynamicsUsageFlags newContentTypes)andUpdateCollisionTags(string[] newCollisionTags).- Remember that a hard limit of 16 tags applies to Contacts. If you try to set more than 16 tags, only the first 16 will apply.